Nuxt3とTypeScriptを使用したプロジェクトにJestを導入し、GitHub Actionsでテストを自動化する手順を解説する。この記事では、Jestのインストールから設定、テストの作成と実行、そしてCI/CDパイプラインに組み込む方法までを詳しく説明する。テストカバレッジレポートの確認方法も紹介するので、プロジェクトの品質向上に役立ててほしい。
実行環境
- Nuxt 3
- TypeScript
Jestインストール
公式: https://jestjs.io/ja/docs/getting-started#typescript-を使用する
まず、Jestをインストールする。
$ npm install --save-dev jest次に、ts-jestをインストールして、TypeScriptを使えるようにする。
npm install --save-dev ts-jest※Jestが、TypeScriptをトランスパイルするために必要な設定ファイル(jest.config.ts)が必要だが、後で解説する。
また、JestのグローバルAPIを使うために、@jest/globalsパッケージもインストールする。
npm install --save-dev @jest/globalsこれで必要なパッケージのインストールは完了。
スクリプトを追加する
次に、package.jsonにJestを実行するためのスクリプトを追加する。
{
"scripts": {
"build": "nuxt build",
"dev": "nuxt dev",
"test": "jest --coverage" // ←追加
},
}
これにより、npm testコマンドでJestを実行できるようになる。
jest.config.tsの作成
プロジェクトのルートにjest.config.tsを作成し、Jestの実行に必要な設定を書いていく。
私のプロジェクトには、PlaywrightのE2Eテストも含まれているため、testPathIgnorePatternsでE2Eテスト対象のファイルをJestの実行から除外している。
詳細は、コードのコメントを参照。
import type { Config } from "jest";
const config: Config = {
collectCoverage: true,
// カバレッジレポートの形式を指定する。
// textはコンソールに出力し、lcovはHTML形式でレポートを生成
coverageReporters: ["text", "lcov"],
// カバレッジレポートを出力するディレクトリを指定
coverageDirectory: "./coverage",
// 特定のファイルを除外
testPathIgnorePatterns: [
"/node_modules/",
"/tests/e2e/", // PlaywrightのE2Eテストがあるディレクトリを除外
],
// transform設定は、Jestがテスト対象のファイルを実行する前に、
// 特定の種類のファイルをどのように変換(トランスパイル)するかを指定するもの
transform: {
"^.+\\.ts$": "ts-jest", // .tsファイル(TypeScriptファイル)をトランスパイルするための設定
"^.+\\.js$": "babel-jest", // .jsファイル(JavaScriptファイル)をトランスパイルするための設定
},
moduleNameMapper: {
// スタイルファイルを無視
"\\.(css|less|scss|sass)$": "identity-obj-proxy",
// エイリアスを解決
// 「~」「@」がプロジェクトのルートディレクトリを指すように設定
"^~/(.*)$": "<rootDir>/$1",
"^@/(.*)$": "<rootDir>/$1",
},
};
module.exports = config;
tsconfig.jsonの設定
verbatimModuleSyntaxオプションを追記する。
{
"extends": "./.nuxt/tsconfig.json",
"compilerOptions": {
"esModuleInterop": true,
// 追記
"verbatimModuleSyntax": false
// その他のオプション...
}
}
verbatimModuleSyntaxオプションは、TypeScriptのコンパイル時にESM(ECMAScript Modules)構文をそのまま保持するかどうかを制御する。ここでは、falseを指定しているため、TypeScriptは、モジュール構文を適切なモジュールシステム(CommonJSやAMDなど)に変換する。
テストの作成と実行
テスト関数
Nuxt3でComposable関数をテストする想定で、composables/useJest.tsを作成する。
export function useJest() {
const message = "Hello, Jest with Nuxt 3!";
const getMessage = () => {
return message;
};
return {
getMessage,
};
}
次に、上記の関数をテストするために、tests/unit/useJest.spec.tsにテストを作成する。
import { describe, expect, test } from "@jest/globals";
import { useJest } from "~/composables/useJest";
describe("useJest Composable", () => {
test("should return the correct message", () => {
const { getMessage } = useJest();
expect(getMessage()).toBe("Hello, Jest with Nuxt 3!");
});
});
テストを実行する。
$ npm test実行結果は以下の通り。
> test
> jest --coverage
Determining test suites to run
PASS tests/unit/useJest.spec.ts
useJest Composable
✓ should return the correct message (1 ms)
-|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
| % Stmts | % Branch | % Funcs | % Lines | Uncovered Line #s
-|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
| 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
-|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
Test Suites: 1 passed, 1 total
Tests: 1 passed, 1 total
Snapshots: 0 total
Time: 1.456 s
テストが成功していることがわかる。
失敗した場合のテストも行ってみる。tests/unit/useJest.spec.tsに以下を追記する。
// 失敗するテスト
test("Failed correct message", () => {
const { getMessage } = useJest();
expect(getMessage()).toBe("Hello, Jest with Next.js!");
});
もう一度、テストを実行する。
$ npm test実行結果は以下の通り。
> test
> jest --coverage
Determining test suites to run
FAIL tests/unit/useJest.spec.ts
useJest Composable
✓ should return the correct message (1 ms)
✕ Failed correct message (2 ms)
● useJest Composable › Failed correct message
expect(received).toBe(expected) // Object.is equality
Expected: "Hello, Jest with Next.js!"
Received: "Hello, Jest with Nuxt 3!"
10 | test("Failed correct message", () => {
11 | const { getMessage } = useJest();
> 12 | expect(getMessage()).toBe("Hello, Jest with Next.js!");
| ^
13 | });
14 | });
15 |
at Object.<anonymous> (tests/unit/useJest.spec.ts:12:26)
-|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
| % Stmts | % Branch | % Funcs | % Lines | Uncovered Line #s
-|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
| 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
-|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
Test Suites: 1 failed, 1 total
Tests: 1 failed, 1 passed, 2 total
Snapshots: 0 total
Time: 2.626 s
1つのテストが成功し、もう1つが失敗していることがわかる。
カバレッジレポートを確認する
テストが完了すると、プロジェクトのルートディレクトリにあるcoverageフォルダにカバレッジレポートが生成される。coverage/lcov-report/index.htmlというHTMLファイルが生成されるので、このファイルをブラウザで開くことで、テストカバレッジの詳細なレポートを確認できる。
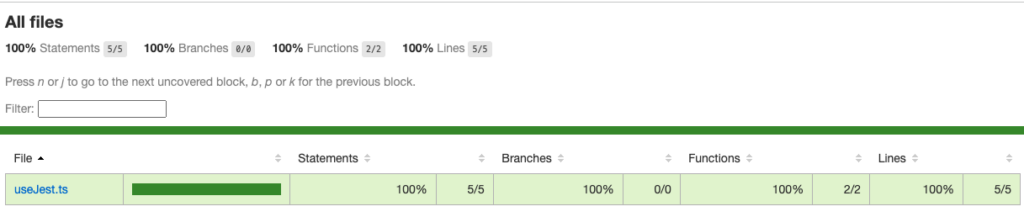
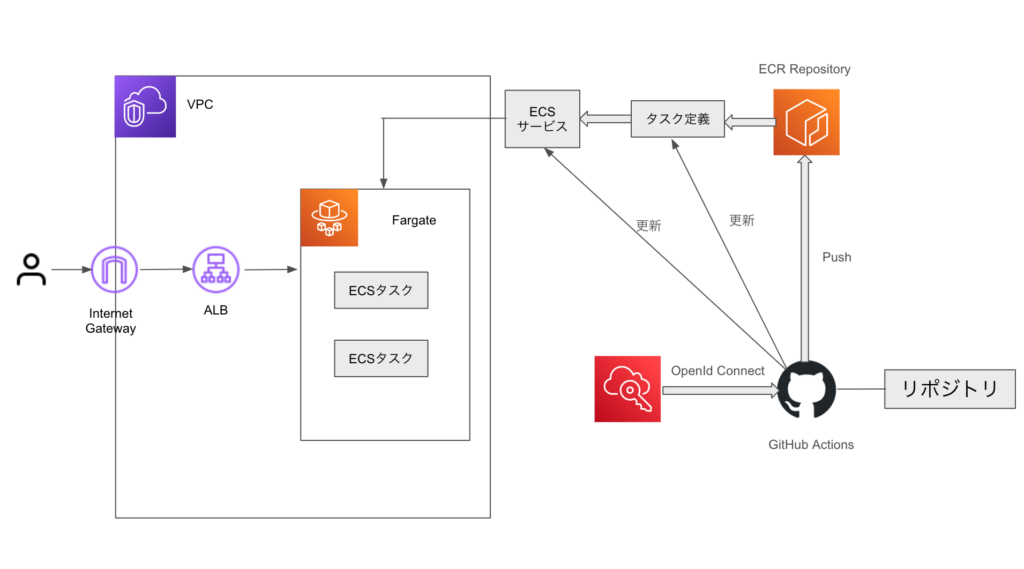
CIで実行する
JestをCIで実行し、GitHub Actionsでカバレッジを確認する方法を紹介する。まず、.github/workflows/ci.ymlを作成し、以下の内容を実装する。
name: CI
on:
push:
branches:
- main
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: "18"
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
# Jestのテストとカバレッジ計測を行う
# coverageディレクトリにカバレッジレポートが出力される
- name: Run tests with coverage
run: npm test -- --coverage
- name: Upload coverage report
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: coverage-report
path: ./coverage/lcov-report
retention-days: 7 # オプション: アーティファクトの保持期間を設定
対象ブランチ(main)にプルリクエストをマージし、CIでテストを実行する。
CIでのテストが成功していることがわかる。
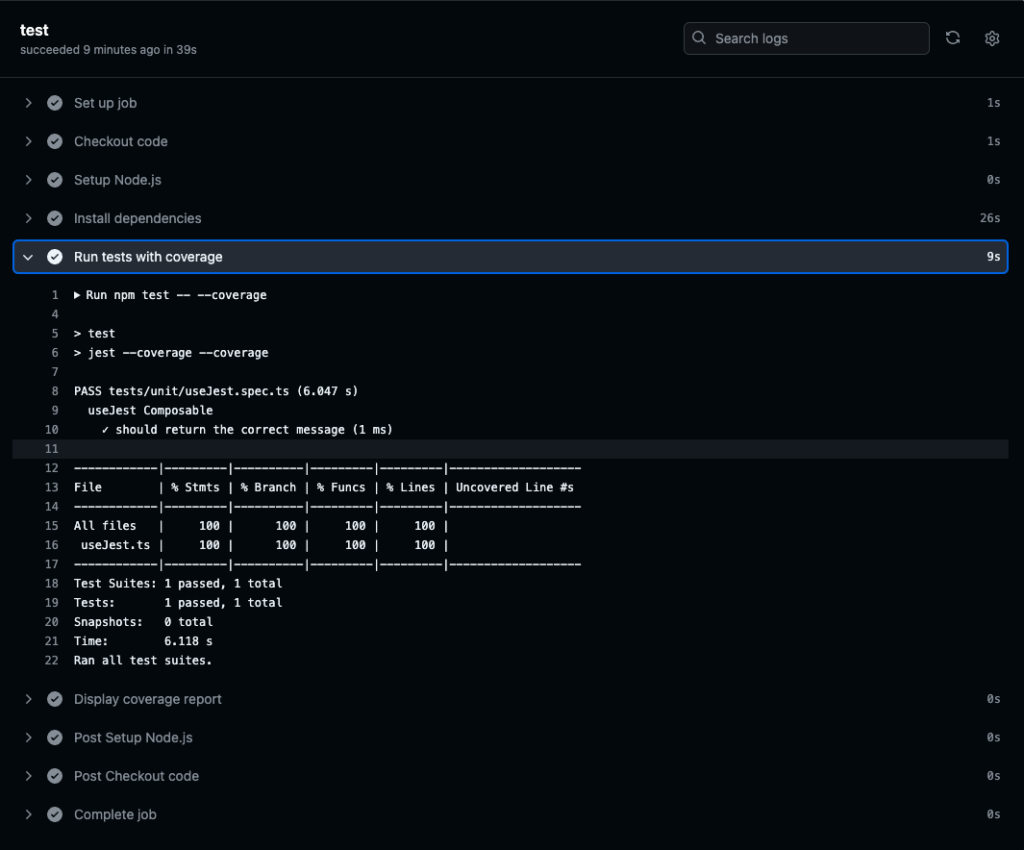
「Upload coverage report」のプロセスで、カバレッジレポートをアーティファクトとしてダウンロードできるように設定している。ファイルをダウンロードすることで、レポートを確認できる。
まとめ
Nuxt 3とTypeScriptを使用したプロジェクトにJestを導入し、テストを自動化する手順を解説した。Jestのインストールから設定、テストの作成と実行、そしてCI/CDパイプラインへの組み込みまで、一連の流れを理解して実践することで、プロジェクトの品質を効果的に向上させることができる。


コメント